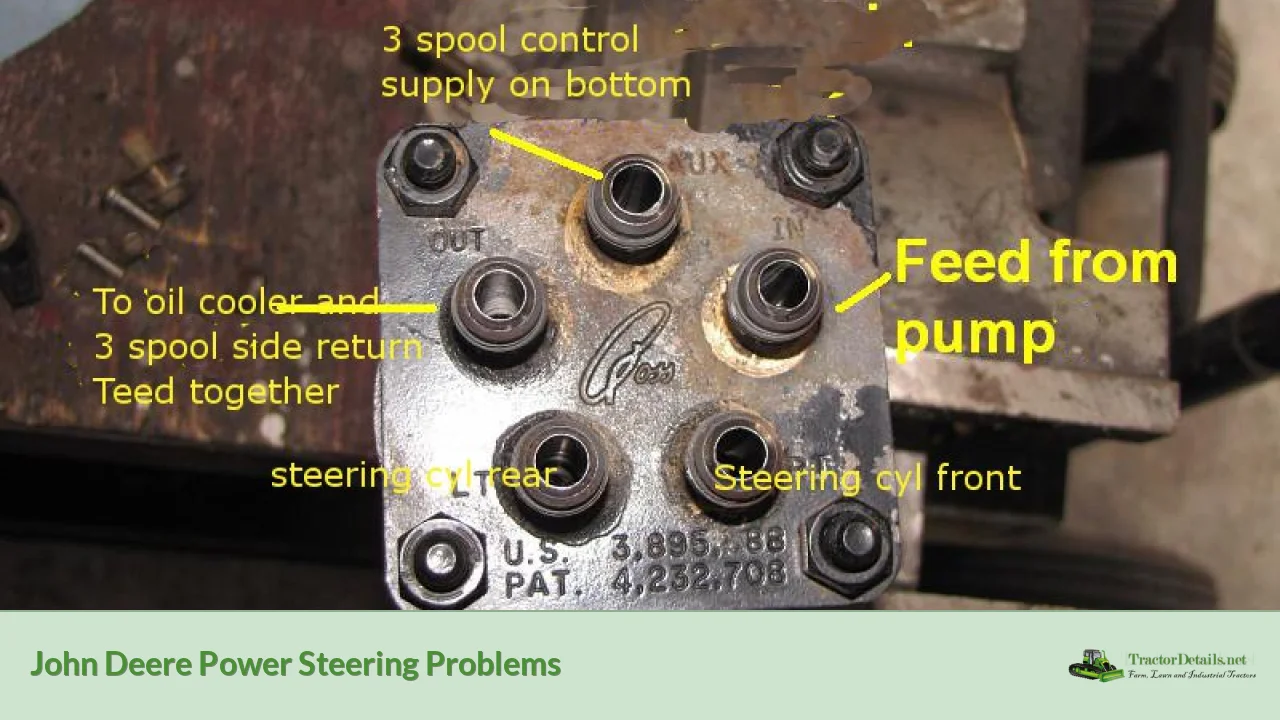
John Deere tractors and mowers are renowned for their durability and performance, but like any machinery, they can experience issues over time. One common problem that many users face is related to power steering. This system is essential for easy maneuverability, especially in larger tractors and riding mowers. When power steering fails or becomes sluggish, it can lead to a frustrating experience for operators. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and solutions to power steering problems is crucial for maintaining the efficiency of your John Deere equipment.
Power steering issues can manifest in various ways, including difficulty in turning the steering wheel, unusual noises while steering, or a complete loss of power steering assistance. These problems can stem from several factors such as low fluid levels, air in the hydraulic lines, worn components, or even issues with the hydraulic pump itself. Identifying the root cause of the problem is essential for effective troubleshooting and repair.
The following table summarizes common symptoms and potential causes of power steering problems in John Deere equipment:
| Symptoms | Potential Causes |
|---|---|
| Difficulty turning the wheel | Low fluid levels or air in lines |
| Noisy steering operation | Worn gears or pump issues |
| Delayed response when turning | Faulty hydraulic pump or cylinder |
| Fluid leaks | Damaged hoses or seals |
| Steering feels heavy | Blocked filters or low hydraulic pressure |
Common Symptoms of Power Steering Issues
Recognizing the symptoms of power steering problems is the first step toward addressing them effectively. Operators should be vigilant about any changes in how their equipment handles.
- Difficulty Turning: If you notice that turning the steering wheel requires significantly more effort than usual, this could indicate low hydraulic fluid levels or air trapped in the system.
- Noisy Operation: Unusual sounds such as whining or grinding when turning can suggest that components like the steering pump or gears are worn out.
- Delayed Response: If there’s a noticeable lag between turning the wheel and the wheels responding, this may point to a failing hydraulic pump or issues within the steering cylinder.
- Fluid Leaks: Inspecting for leaks around hoses and connections is crucial. Leaking hydraulic fluid can severely impact performance.
- Heavy Steering Feel: A sudden increase in steering resistance may indicate a blockage in filters or low hydraulic pressure due to various reasons.
Understanding these symptoms will help operators diagnose their equipment more accurately and take appropriate action.
Troubleshooting Power Steering Problems
When faced with power steering issues, systematic troubleshooting can help identify and resolve the problem quickly. Here are some steps to follow:
1. Check Fluid Levels: Begin by inspecting the hydraulic fluid reservoir. Low fluid levels can lead to inadequate pressure, causing steering difficulties. Top up with the recommended fluid if necessary.
2. Inspect for Leaks: Look for any visible signs of leaks around hoses, fittings, and seals. If leaks are found, they must be repaired before further troubleshooting.
3. Bleed the System: Air trapped in the hydraulic lines can cause erratic steering behavior. Bleeding the system involves loosening a bleed screw on the cylinder while someone turns the wheel back and forth to allow trapped air to escape.
4. Examine Components: Check components such as the steering pump, control valves, and cylinders for wear or damage. Replacing worn parts may restore proper function.
5. Test Hydraulic Pressure: If problems persist after checking fluid levels and bleeding air, it may be necessary to test hydraulic pressure using a gauge to ensure it meets specifications.
6. Consult Technical Manuals: Refer to your equipment's technical manual for specific troubleshooting procedures related to your model's power steering system.
By following these steps methodically, operators can often pinpoint and rectify power steering issues without extensive repairs.
Common Causes of Power Steering Failures
Understanding what typically causes power steering failures can help prevent future problems. Here are some common culprits:
- Low Hydraulic Fluid: Insufficient fluid levels are one of the most frequent causes of power steering failure. This can happen due to leaks or neglecting routine maintenance.
- Air in Hydraulic Lines: Air trapped within the system can disrupt fluid flow, leading to sluggish or unresponsive steering.
- Worn Components: Over time, parts such as gears, pumps, and cylinders can wear out due to regular use. This wear can lead to inefficiencies in how well the system operates.
- Hydraulic Pump Failure: The pump is responsible for generating pressure within the system. If it fails or becomes inefficient, it will directly affect steering performance.
- Clogged Filters: Dirty filters can restrict fluid flow within the system, leading to reduced pressure and performance issues.
Addressing these causes promptly through regular maintenance checks can extend the lifespan of your power steering system.
Maintenance Tips for Power Steering Systems
Regular maintenance is vital for ensuring that your John Deere's power steering system operates smoothly. Here are some essential maintenance tips:
- Regular Fluid Checks: Frequently check hydraulic fluid levels and top up as needed using manufacturer-recommended fluids.
- Inspect Hoses and Fittings: Regularly examine hoses and fittings for signs of wear or damage that could lead to leaks.
- Change Filters Periodically: Follow manufacturer guidelines on filter replacement schedules to prevent clogging that could impair performance.
- Bleed System Regularly: If you notice any changes in responsiveness, consider bleeding your power steering system periodically as part of routine maintenance.
- Lubricate Moving Parts: Ensure that all moving components within the steering assembly are adequately lubricated to reduce friction and wear over time.
Implementing these maintenance practices will help keep your power steering system functioning optimally and reduce the likelihood of unexpected failures.
Repairing Power Steering Problems
If troubleshooting indicates that repairs are necessary, understanding what repairs might be required is essential:
- Replacing Worn Parts: If components such as gears or pumps are found to be worn out during inspection, replacing them with OEM parts will ensure compatibility and reliability.
- Fixing Leaks: Repairing damaged hoses or seals is crucial if leaks are detected; otherwise, even new parts may fail prematurely due to insufficient fluid pressure.
- Rebuilding Hydraulic Pumps: In cases where pumps have failed but show signs of minor wear, rebuilding them may be a cost-effective solution compared to complete replacement.
- Adjusting Control Valves: Sometimes control valves may require adjustment rather than replacement if they have become misaligned over time due to wear.
Taking immediate action on identified issues will prevent further complications down the line and maintain optimal performance of your equipment.
FAQs About John Deere Power Steering Problems
- What should I do if my John Deere's power steering stops working?
Check fluid levels first; if low, refill with recommended hydraulic fluid. - How often should I check my power steering fluid?
It’s advisable to check at least once a month during regular maintenance. - Can I drive my John Deere with a faulty power steering?
No; driving with faulty power steering can lead to further damage and safety risks. - What is causing my John Deere's power steering to make noise?
Noise typically indicates worn gears or a failing pump; inspection is needed. - How do I bleed air from my John Deere's power steering?
Loosen a bleed screw while turning the wheel back and forth until air escapes.
By understanding these aspects of John Deere power steering systems—symptoms, causes, troubleshooting steps, maintenance tips, repair options—you'll be better equipped to handle any issues that arise efficiently. Regular attention will ensure your equipment remains reliable for years to come.